The diabetes diagnosis is by blood sugar tests. Diabetes diagnosing tests are Fasting Plasma Glucose FPG test, Oral Glucose Tolerance OGT test (most emphasized), Random plasma glucose test (not reliable) and A1C.
Diabetes screening criteria
Below are the set of rules for suggesting diabetes screening.
Criteria for diabetes diagnosis are:
- More than two diabetes risk factors,
- Central obesity,
- Have had gestational diabetes,
- Already diagnosed as pre-diabetes,
- Presence of diabetes symptoms,
- Have hypertension or high blood pressure,
- Have hyperlipidemia or high blood cholesterol.
If you met most of the above-said criteria, then you need to undergo diabetes screening.
How is diabetes diagnosis?
Blood tests are used to diagnosis diabetes; there are several ways to diagnose diabetes. They are fasting blood glucose test, oral glucose tolerance test, and glycated hemoglobin A1C test.
If the test result indicates that a person has diabetes, then should be re-confirming with a second test on a different day. What is pre-diabetes? The blood glucose is higher than normal but not high enough to diagnose diabetes. Pre-diabetes puts you at risk for developing type 2 diabetes.
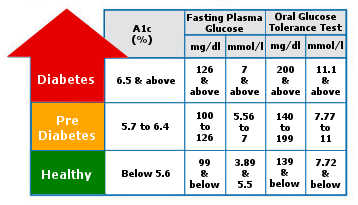
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) – is a blood-glucose test after not having anything to eat or drink (except water - even do not drink a lot of water before the test) a minimum of eight hours before the test. This test is conveniently carried out in the morning, before breakfast. Confirm diabetes diagnosis if BS is greater than or equal to 126 mg/dl (7 mmol/L). Diagnose as pre-diabetes if BS is 100 mg/dl to 126 mg/dl (5.56 to 7 mmol/L). Confirm hypoglycemia if BS level is lower than 70 mg/dl (3.89 mmol/L).
- Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) – is a glucose challenge test by testing blood glucose level before food and two hours after a carbohydrate-rich food or a special sweet drink. Confirm diabetes if BS is greater than or equal to 200 mg/dl (11.1 mmol/L). Diagnose as pre-diabetes if BS is 140 mg/dl to 199 mg/dl (7.77 to 11 mmol/L).
- Random plasma glucose test – is a blood glucose test at any time of the day no restrictions. Confirm diabetes diagnosis if the BS is greater than or equal to 200 mg/dl (11.1 mmol/L).
- Glycated hemoglobin test (A1C) – is a test to measure the average BS for the past two to three months. You can undergo this test at any time; there is no fast required; you can eat or drink anything. Confirm diabetes diagnosis if the A1C percentage is greater than or equal to 6.5%. Diagnose as pre-diabetes if the A1C is 5.7% to 6.4%.
What test is preferable in early diabetes diagnosis?
Why do most patients diagnose as diabetes, along with complications? You can find an answer to this question from this study. "Impaired fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance, what best predicts future diabetes in Mauritius," was published in Diabetes Care March 1999 vol. 22 no. Three 399-402. It shows the higher sensitivity of IGT over IFG for predicting progression to type2 diabetes. Screening by the criteria for IFG alone would identify fewer people who subsequently, progress to type2 diabetes than would be the oral glucose tolerance test.
Thus, it is preferable to take both IFG & IGT tests for early diagnosis of diabetes. However, most doctors chose only IFG for diagnosis. Therefore high percentages of people with IGT have missed out from diagnosis.
BS number once confirms diabetes, and next proved wrong, why?
People getting different results between tests may indicate diabetes is trying to get through the system. Where blood-glucose levels have not risen high enough or not yet stabilizes to be higher level to show up on every test result.
For many, making few lifestyle changes such as losing some weight, increase in physical activity, and eat healthily can help reverse diabetes or at least delay its onset.

