The National Health Interview Survey found 22 % of people with diabetes used herbal remedies!
As per ancient literature, more than 800 plants have anti-diabetic properties, which indicates that diabetes has existed since the prehistoric age.
Various hypoglycemic effects of diabetes herbs
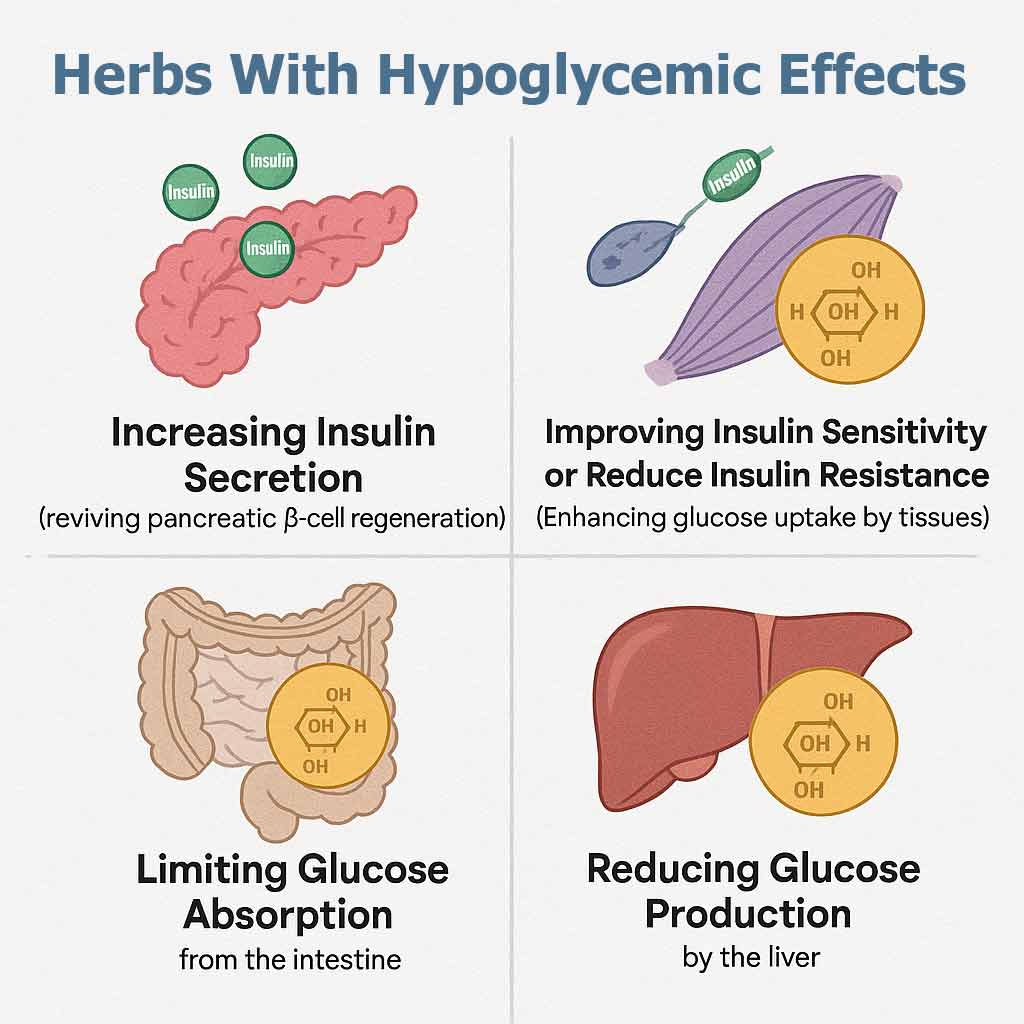
Diabetes herbs possess hypoglycemic effects through several modes of action, which can be classified into four groups:
- Increasing insulin secretion (reviving pancreatic β-cell regeneration),
- Improving Insulin Sensitivity or reducing insulin Resistance (Enhancing glucose uptake by tissues),
- Limiting glucose absorption from the intestine, and
- Reducing glucose production by the liver.
1. Reviving Pancreatic β-cell regeneration (Enhancing Insulin Secretion)
Beta cells in the pancreas are responsible for producing insulin, and their rejuvenation is crucial for those dealing with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. While there is no magic herb that can fully regenerate beta cells, several herbs and natural compounds have been suggested to help support pancreatic health and aid in the overall functioning of beta cells.
Here are some herbs and natural remedies that might support beta cell rejuvenation or overall pancreatic function: Ginseng (Panax ginseng), Bitter Melon (Momordica charantia), Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum), Berberine (Berberis species), Gymnema Sylvestre, and Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera).
2. Improving Insulin Sensitivity or Reducing Insulin Resistance (Enhancing Glucose Uptake by Tissues)
Insulin sensitivity is important because it helps the body use insulin effectively, which is crucial for managing blood sugar levels. If someone has low insulin sensitivity, they might be at risk for developing type 2 diabetes or having trouble managing it if they already have it.
Improving insulin sensitivity is crucial for managing blood sugar levels, especially for individuals with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes. Certain herbs may reduce insulin resistance by promoting glucose uptake in tissues, making insulin more effective. The process relies on ensuring that cells (especially muscle and fat cells) can effectively absorb glucose in response to insulin. While they can’t replace medication or lifestyle changes, they can complement a healthy routine.
Here are some of the most effective herbs known to help improve insulin sensitivity: Cinnamon (Cinnamomum cassia), Gymnema Sylvestre, Berberine (Berberis species), Turmeric (Curcuma longa), Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum), Bitter Melon (Momordica charantia), Ginseng (Panax ginseng), Black Seed (Nigella sativa), Clove (Syzygium aromaticum), and Green Tea (Camellia sinensis).
3. Inhibiting Glucose Absorption from the Intestine
Some herbal preparations contain compounds that inhibit enzymes responsible for breaking down carbohydrates in the digestive tract. For example, α-glucosidase inhibitors derived from certain plants can slow down carbohydrate digestion and absorption in the intestines, leading to a more gradual increase in blood sugar levels after meals, making it a target for managing postprandial hyperglycemia.
Here are some herbs that may help inhibit glucose absorption from the intestine: Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum), Ginseng (Panax ginseng), Bitter Melon (Momordica charantia), Berberine (Berberis species), Ginseng (Panax ginseng), Bitter Melon (Momordica charantia), Berberine (Berberis species), Cinnamon (Cinnamomum cassia), Turmeric (Curcuma longa), and Clove (Syzygium aromaticum).
4. Inhibiting Glucose Production by the Liver
Inhibiting glucose production by the liver is a key strategy in managing blood sugar levels. The liver produces glucose through a process called gluconeogenesis, which can be excessive in individuals with impaired insulin function, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Here are some herbs that have shown potential in inhibiting liver glucose production: Berberine (Berberis species), Cinnamon (Cinnamomum cassia), Turmeric (Curcuma longa), Gymnema Sylvestre, Silymarin (Milk Thistle), Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum), Black Seed (Nigella sativa), and Ginseng (Panax ginseng).
Caution when you decide to use diabetes herbs
When considering herbal treatments for diabetes, it's crucial to:
- Consult with a healthcare provider because herbs can interact with diabetes medications or have side effects.
- Use them as part of a comprehensive management plan that includes diet, exercise, and possibly conventional medication.
- Remember that the effectiveness can vary widely among individuals, and scientific evidence supporting the use of herbs for diabetes management is still growing and sometimes mixed.
- Herbal remedies should not replace conventional medical treatment without professional advice due to the complexity of managing diabetes.
Herb useful for diabetes

Ginseng (Panax ginseng)
Ginseng improves insulin sensitivity and helps protect pancreatic beta cells from oxidative stress and inflammation. It could promote beta-cell regeneration. Ginseng inhibits the absorption of glucose by slowing down the activity of digestive enzymes alpha-glucosidase. It is also shown to inhibit glucose production in the liver by improving insulin sensitivity and modulating glucose metabolism.
Usage: Ginseng can be taken in capsule, powder, or tea form. A typical dose is around 200–400 mg per day.
Bitter Melon (Momordica charantia)
Bitter melon is known to improve insulin secretion and may aid in the regeneration of beta cells. It contains compounds that mimic insulin, which can help lower blood glucose levels and promote beta cell regeneration. Bitter melon may reduce glucose absorption in the intestines and help lower blood sugar levels.
Usage: Bitter melon can be consumed as a vegetable, juice, or in supplement form. A typical dose of bitter melon extract is 500–1,000 mg per day.
Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum)
Fenugreek seeds contain compounds like 4-hydroxyisoleucine, which may help in improving insulin secretion and sensitivity, and reduce hepatic glucose production by modulating the activity of enzymes involved in gluconeogenesis. It contains high amounts of soluble fiber, which can help slow down the absorption of sugar and improve insulin sensitivity. Some studies suggest that it could promote beta-cell regeneration in animal models.
Usage: Fenugreek seeds can be taken in powder form (1–2 teaspoons per day) or as a supplement.
Berberine (Berberis species)
Berberine is a bioactive compound found in several plants, including Goldenseal and Oregon Grape. Berberine has also shown some potential in protecting and regenerating beta cells in animal studies. It inhibits enzymes like alpha-glucosidase, which slows the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates. By activating AMPK, berberine helps reduce hepatic gluconeogenesis.
Usage: A typical dose of berberine is 500 mg, taken 2–3 times per day. However, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider as berberine can interact with other medications.
Gymnema Sylvestre
Gymnema Sylvestre may help in reducing sugar absorption in the intestines and improving insulin secretion. Some studies indicate that it can support the regeneration of beta cells. It also inhibits glucose production in the liver by modulating the activity of key enzymes involved in gluconeogenesis.
Usage: Gymnema is typically taken in the form of capsules (200–400 mg) or as a tea.
Ashwagandha
Ashwagandha is an adaptogen that may reduce stress, which can indirectly support insulin production and beta cell health. It also has anti-inflammatory effects and could improve overall pancreatic function.
Usage: Ashwagandha is typically consumed in capsule form, with doses ranging from 300–500 mg per day.
Cinnamon (Cinnamomum cassia)
Cinnamon contains compounds like cinnamaldehyde and polyphenols that can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce glucose production in the liver by reducing the activity of digestive enzymes such as amylase and glucosidase. Studies suggest that cinnamon can lower blood sugar levels and enhance insulin function.
Usage: You can add ground cinnamon to your smoothies, oatmeal, or tea. The typical dose for supplementation is around 1–2 teaspoons per day.
Turmeric (Curcuma longa)
Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, has potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, thus helping improve insulin sensitivity. It can help inhibit enzymes involved in carbohydrate breakdown, reducing the rate at which glucose is absorbed. It is shown to reduce hepatic glucose production by inhibiting the expression of key enzymes involved in gluconeogenesis.
Usage: Add turmeric to your cooking or take it as a supplement. A common dose of curcumin is 500–1,000 mg per day.
Black Seed (Nigella sativa)
Black seed contains thymoquinone, a compound that has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, thus improving insulin sensitivity and reducing blood sugar levels. Thymoquinone has been shown to help regulate glucose production in the liver by inhibiting the activity of enzymes involved in gluconeogenesis.
Usage: Black seed oil or ground black seed can be taken in doses of 1–2 teaspoons per day.
Green Tea (Camellia sinensis)
Green tea contains catechins, particularly epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which have been shown to improve insulin sensitivity by enhancing glucose metabolism and reducing fat accumulation in the liver.
Usage: Drink 2–3 cups of green tea per day or take green tea extract in supplement form (250–500 mg daily).
Clove (Syzygium aromaticum)
Clove has compounds like eugenol that may help reduce glucose absorption by inhibiting digestive enzymes involved in carbohydrate breakdown. It can also improve insulin sensitivity. Clove is a powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory herb, which may help reduce insulin resistance.
Usage: You can add ground clove to your food, tea, or use clove oil in moderation.
Silymarin (Milk Thistle)
Silymarin, the active compound in milk thistle, has been shown to reduce hepatic glucose production by improving liver function. It helps decrease oxidative stress in the liver, which is a key contributor to excessive glucose production. Silymarin may also support insulin sensitivity. It is a potent liver protectant and antioxidant that can help reduce inflammation and promote liver regeneration.
Usage: The typical dose of silymarin is 200–400 mg per day, taken in supplement form.