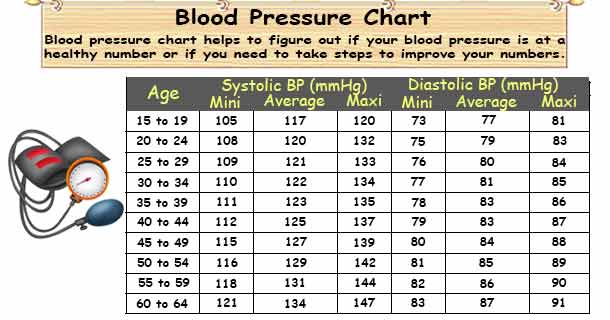
Blood pressure chart on this page can be helpful to figure out if your blood pressure is at a healthy number or if you need to take steps to improve your numbers.
Blood pressure reading includes systolic and diastolic pressure values. Systolic blood pressure is the peak pressure when the heart contracts while pumping blood. Diastolic blood pressure is the drop in force when the heart is at rest between beats.
Often blood pressure is noted as the systolic number above or before the diastolic, such as 120/80 mmHg. (The mmHg is millimeters of mercury, the unit to measure pressure.)
Blood Pressure Chart by Age
Naturally, aging loses the elasticity of the arteries. Thus blood pressure rises with age. The blood pressure chart on this page provides blood pressure related to age.
We came to know through medical studies that there is a thumb rule for the systolic number is 100 plus your age for men (100 plus age minus 10 for female).
The study SPRINT (Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial) found that when systolic blood pressure was lowered to below 120 mmHg, there was a 27 % reduction in mortality from all causes compared to below 140 mmHg.
Some modern physicians thought that healthy blood pressure reading is 120/80 mmHg regardless of any consideration for age. Yes, it is always better to manage this number without considering the age. However, if you find hurdles, then it is ok for you to relax your target a little based on age.
Eight blood pressure categories or classifications
Eight blood pressure categories are as below (in mmHg):
- Optimal BP – Below 120 (SBP) & 80 (DBP). Best or most favorable blood pressure range. This range is good for your heart, kidney, other internal organs, and for overall health.
- Normal BP – Below 130 (SBP) & 85 (DBP). Blood pressure range noted among most healthy individuals. Even if it is not optimal, it is still considering a good number. Keep it up, stick with a healthy diet, and doing regular exercise.
- Prehypertension – Within 130 to 139 (SBP) & 85 to 89 (DBP). Prehypertension is considering as an alarm that you may develop hypertension at any time. Prehypertension individuals are likely to develop high blood pressure unless you introduce necessary healthy habits.
- Grade 1 HTN – Within 140 to 159 (SBP) & 90 to 99 (DBP). Stage 1 hypertension individual needs lifestyle changes and may consider taking blood pressure medication.
- Grade 2 HTN – Within 160 to 179 (SBP) & 100 to 109 (DBP). Stage 2 hypertension individual needs to take combination hypertension medication along with healthy lifestyle changes.
- Grade 3 HTN – Above 180 (SBP) & 110 (SBP). Stage 3 hypertension individual require immediate emergency medical care.
- Isolated systolic HTN (grade 1) – SBP within 140 to 159 & DBP below 90. Stage 1 isolated systolic hypertension individuals require a lifestyle change and may consider taking hypertension drugs. Care should be taken to avoid DBP less than 55 mm Hg in older patients with ISH.
- Isolated systolic HTN (grade 2) – SBP above 160 & DBP below 90. Stage 1 isolated systolic hypertension individuals require a lifestyle change and may consider taking hypertension drugs. Care should be taken to avoid DBP less than 55 mm Hg in older patients with ISH.
What blood pressure category you belong?
When systolic and diastolic blood pressures fall into different categories, you should use the higher category to classify blood pressure levels. For example, 150/79 mmHg would be stage 1 hypertension.
Also, you can consider hypertension even if you one number is high regardless of the other. If your systolic number is 140 or more, you may have hypertension, also if your diastolic number is healthy. If your diastolic number is 90 or more, you may have hypertension, even if your systolic number is healthy.