Blood pressure staying in-between 120/80 mmHg and 139/89 mmHg is considering as pre-hypertension, based on 2 or more properly measured seated BP readings on each of 2 or more office visits. It is not a high blood pressure, but likely to develop in the future. Still, it is possible to prevent high blood pressure by adopting a healthy lifestyle.
About 1 in 3 American adults has prehypertension (Blood pressure between 130/85 to 139/89 mmHg), not high enough to diagnose as hypertension.
What is pre-hypertension?
The study shows 2/3 of prehypertension have progressed to stage-1 hypertension within four years. Prehypertension tends to cluster with other cardiovascular risk factors such as diabetes, cholesterol, etc. Obesity and weight gain is the major contributing factor for the progression towards hypertension or its complications.
Prehypertension is considering as an alarm that you may develop hypertension at any time soon. Prehypertension individuals are likely to develop high blood pressure unless you introduce necessary healthy habits.
Prehypertension risk/effects
Does prehypertension cause any damage if not develop into hypertension? High-normal blood pressure is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Reference: Impact of High-Normal Blood Pressure on the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease, published in The New England Journal of Medicine 2001; 345:1291-1297
Why should pre-hypertension take seriously? The clinical studies data show the risk towards cardiovascular events; mortality is doubling with 20 mm Hg increases in systolic, and 10 mm Hg increases in the diastolic beginning with a BP of 115/75 mm Hg. The risk is higher for individuals with diabetes mellitus or chronic kidney disease.
According to 2005 the Framingham heart study, men with prehypertension have 3.5 times more chances to have a heart attack than those with normal blood pressure. Surprisingly, prehypertension does not appear to increase the stroke risk.
Newly diagnosed as prehypertension! What to do next?
Once you have diagnosed as prehypertension, be vigilant so that you can avoid hypertension and cardiovascular risk.
- You should know that your BP is slightly high (optimal is less than 120/80 mmHg).
- You got the warning of hypertension; you will have more chances to develop into hypertension than those with normal BP.
- You have to take necessary steps to avoid hypertension with lifestyle modification.
- You have to assess your other cardiovascular risks by testing fasting lipid profile, fasting blood-glucose level, renal profile and ECG.
- Arrange a follow-up visit once in three to six months.
Does prehypertension need medicinal treatment?
What are the ways to reverse prehypertension without medication? Prehypertension guidelines do not recommend drug therapy unless otherwise there is a requirement by an additional condition such as diabetes or chronic kidney disease.
You should start your prehypertension treatment with therapeutic lifestyle intervention or healthy lifestyle modification/changes as follows.
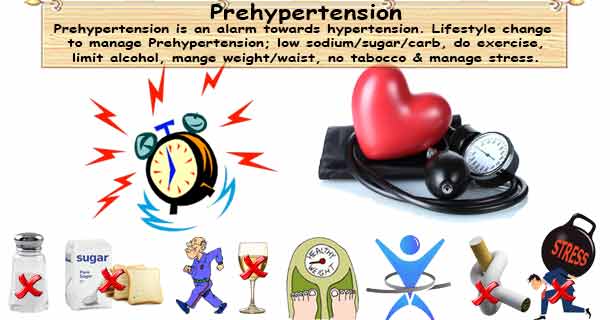
8 Lifestyle Changes Prehypertension
Can I prevent/reverse prehypertension? Yes, you can, you should adhere to hypertension therapeutic lifestyle, which helps to avoid hypertension or even to reverse prehypertension.
- Reduce sodium intake to less than 1500 mg/day. It helps to improve hypertension treatment, 13 percent reduction in cardiovascular disease; a fewer visit to doctor’s office and blood pressure drops by an amount of 5.1/2.7 mmHg.
- Healthy food - Avoid sugar and refined carbohydrates. Take a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy saturated fats. Switching to a healthy diet from an unhealthy diet can lower you BP by about 11.6/5.5 mmHg.
- Regular exercises – 30 to 60 minutes of moderate intensity exercise is requiring for 4 to 7 days per week. Doing 120 to 150 minutes of exercise per week can lower BP by 4.9/3.7 mmHg.
- Your alcohol consumption should not be more than two standard drinks per day or 14 drinks per week for men (or 9 drinks per week for women or lean person). Reducing alcohol consumption can help lower BP by 2 to 4 mmHg.
- Try to achieve or maintain healthy body weight (BMI 18.5-24.9 kg/m2). Weight loss of 1 kg can produce 1.1/0.9 mmHg.
- Maintain healthy waist circumference - Men below 102 cm and Women below 88 cm.
- Stop tobacco usage in any form as well as maintain the tobacco-free environment.
- Stress management – in the case of many hypertension patients, stress is an important contributing factor for elevation in blood pressure. Cognitive-behavioral therapy and relaxation techniques can help a lot in better hypertension management.
Can I drink Coffee if I have prehypertension? Caffeine in the coffee is a mild stimulant that can raise your blood pressure for a short duration; for few minutes to an hour then it returns to normal pressure. Coffee additionally has a diuretic effect, means it remove water from your body, which will lower your blood pressure. So you can drink one or two glasses of coffee per day without any problems. If you drink more, it might elevate your blood pressure permanently.