Although sleep may once be, consider as a steady state, it has several stages that cycle throughout the night.
The brain wave (amplitudes and frequencies) present at a particular time decide the stage of sleep. Most important sleep stage (5th stage) occurs with clear dreams, called the Rapid Eye Moment (REM) stage.
REM sleep has rapid eye movement while dreaming; dreaming occurs even during the other sleep stages, but the most vivid dreaming only happens in REM stage.
REM & NREM Sleep Stage
Sleep follows a certain regular sleep cycle every night. There are two basic forms of sleep: rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. REM sleep can sometimes consider as paradoxical sleep.
Infants have about half of their sleep time in REM sleep. Adults have about 20% of their sleep time in REM, balance NREM sleep.
Older adults have fewer than 15% of their sleep time in REM sleep, balance NREM sleep.
Sleep Cycle
One sleep cycle takes about 90 to 100 minutes; thus for an average sleep time of eight hours, there will be a four to five complete sleep cycles.
The sleep cycle begins with four-stages of sleep called by Slow Wave Sleep (SWS) or non-rapid eye movement (NREM or Non-REM) sleep. After completing the first four stages, instead of continuing to fifth REM sleep the four stages quickly reversed and then followed by REM sleep.
The REM sleep will occur roughly after 90 minutes of falling asleep, and it will last only for about 10 minutes, giving the starting sleep cycle being around 100 minutes. The duration of the stages of sleep is not stable, and it varies. The duration of sleep stages 3 and 4 (also called delta or deep sleep) slowly wanes. On the other hand, the duration of sleep stage 5 (REM sleep) increases, up to about one hour in length after certain sleep cycles. Therefore, as the night continues, the dream may be for longer periods.
Sleep Pattern Summary – One Sleep Cycle
Sleep stage 1
Sleep stage 1 is the light sleep; with drift in and out of sleep, so can wake up easily during this stage. This stage has slow eyes movement and muscle activity. During this stage, many people experience sudden muscle contractions, preceded by a sensation of falling.
Common characteristics of sleep stage one
- the transition between sleep and wakefulness
- eyes roll slightly
- mostly contains theta waves (high amplitude and low frequency – slow wave)
- briefly contains alpha waves, similar to those present while awake
- stage 1 lasts only for a few minutes
Sleep stage 2
Sleep stage 2 has no eye movement; the brain waves become slower and only with an occasional burst of rapid brain waves.
Common characteristics of sleep stage two
- the amplitude of brain wave peaks becomes higher (sleep spindles)
- k-complexes (peaks suddenly descend and then rises) follow spindles
- stage 2 lasts for a few minutes
Sleep stage 3
Sleep stage 3 has slow brain waves called delta waves interspersed with smaller and faster waves. This stage can know as deep sleep, so it is difficult to wake up from this stage.
Common characteristics of sleep stage three
- called as delta sleep or deep sleep
- slow brain waves called delta waves (lower frequency than theta waves)
- 20 - 50% of brain waves are delta waves; the balances are theta waves.
Sleep stage 4
In Sleep stage 4, the brain produces delta waves almost exclusively. This sleep stage has a deep sleep, so it is difficult to wake up at this stage. In this stage, there is no eye movement or muscle activity. In this sleep stage, some children experience bed-wetting, sleepwalking, or night terrors.
Common characteristics of sleep stage four
- called as delta sleep or deep sleep
- More than 50% of brain waves are delta waves; the balances are theta waves.
- Last sleep stages before REM sleep; sleep stages reverse and then REM sleep begins.
Sleep stage 5 - REM
Sleep stage 5 is a REM stage, with more shallow rapid breathing, eyes jerks and paralyzes of limb muscles. The waveform during REM has low amplitudes, high frequencies that are just like a waking state. Early researchers called it "paradoxical sleep.” REM stage has increased heart rate, raised blood pressure, erection in males, and the body does not regulate its temperature. Most of the vivid dreams occur during REM sleep, once awaken at this stage a person can remember the dreams. Most people experience three to five times of REM sleep each night.
Common characteristics of sleep stage five
- beta waves - have a high frequency, and it happens when the brain is active, that is during REM sleep and while awake
- frequent bursts of rapid eye movement, with occasional muscular twitches
- heart beat faster with shallow and rapid breathing
- most vivid dreaming occurs during REM
Infants spent almost 50% of their sleep time in REM stage. Adults spend nearly half of their sleep time in stage 2, about 20% in REM and other 30% has shared between the other three stages. Older adults spend progressively less time in REM sleep.
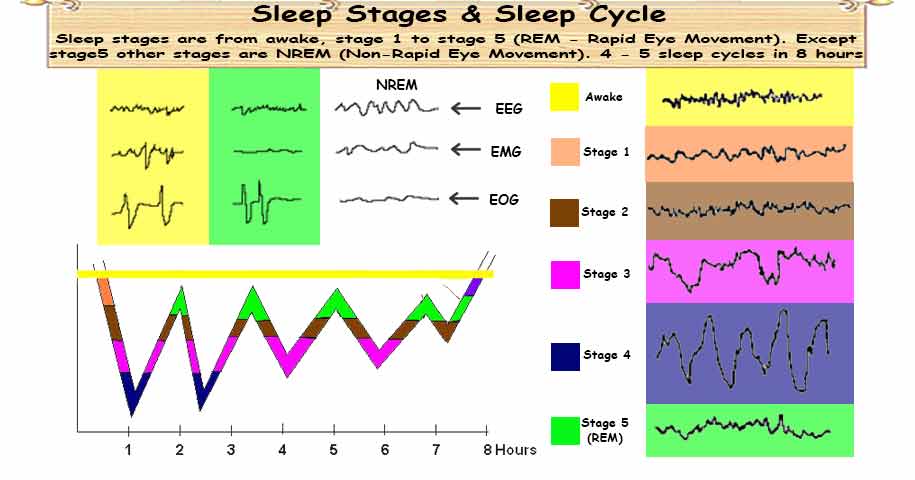
Look at the differences in the EEG (Electro-Encephalo-Gram shows the brain activity), EMG (Electro-Myo-Gram shows the muscle activity) and EOG (Electro-Oculo-Gram shows the eye movements) during waking, REM sleep, and NREM sleep.
Stages of sleep & waveform details
- During awake - the waveform has 15 to 50 Hz frequency and less than 50 microvolts amplitude.
- Pre-sleep - the waveform has 8 to 12 Hz frequency and about 50 microvolts amplitude, it is called as an alpha wave.
- Stage 1 - the waveform has 4 to 8 Hz frequency and 50 to 100 microvolts amplitude, it is called as theta wave.
- Stage 2 - the waveform has 4 to 15 Hz frequency and 50 to 150 microvolts amplitude, it is called as spindle wave.
- Stage 3 - the waveform has 2 to 4 Hz frequency and 100 to 150 microvolts amplitude, it is called as spindle and wave.
- Stage 4 - the waveform has 0.5 to 2 Hz frequency and 100 to 200 microvolts amplitude, it is called as slow and delta wave.
- Stage 5 (REM) - the waveform has 15 to 30 Hz frequency and less than 50 microvolts amplitude.
During asleep, our brain waves pass through different stages of sleep. Start first from stage1 sleep for few minutes; continue to stage2 sleep, stage3 sleep, stage4 sleep. It repeats in the reverse order stage3, stage2, and then REM sleep. After that, it will repeat down and up continuously as shown in the figure. In an 8-hour sleep, the brain cycles through these stages about 4-5 times.